The constellation Libra
Characteristics
- Other names / Symbolism
- Balance
- Hemisphere
- Southern hemisphere
- Visibility
- January - August
- Area
- 538 deg²
- Brightest star
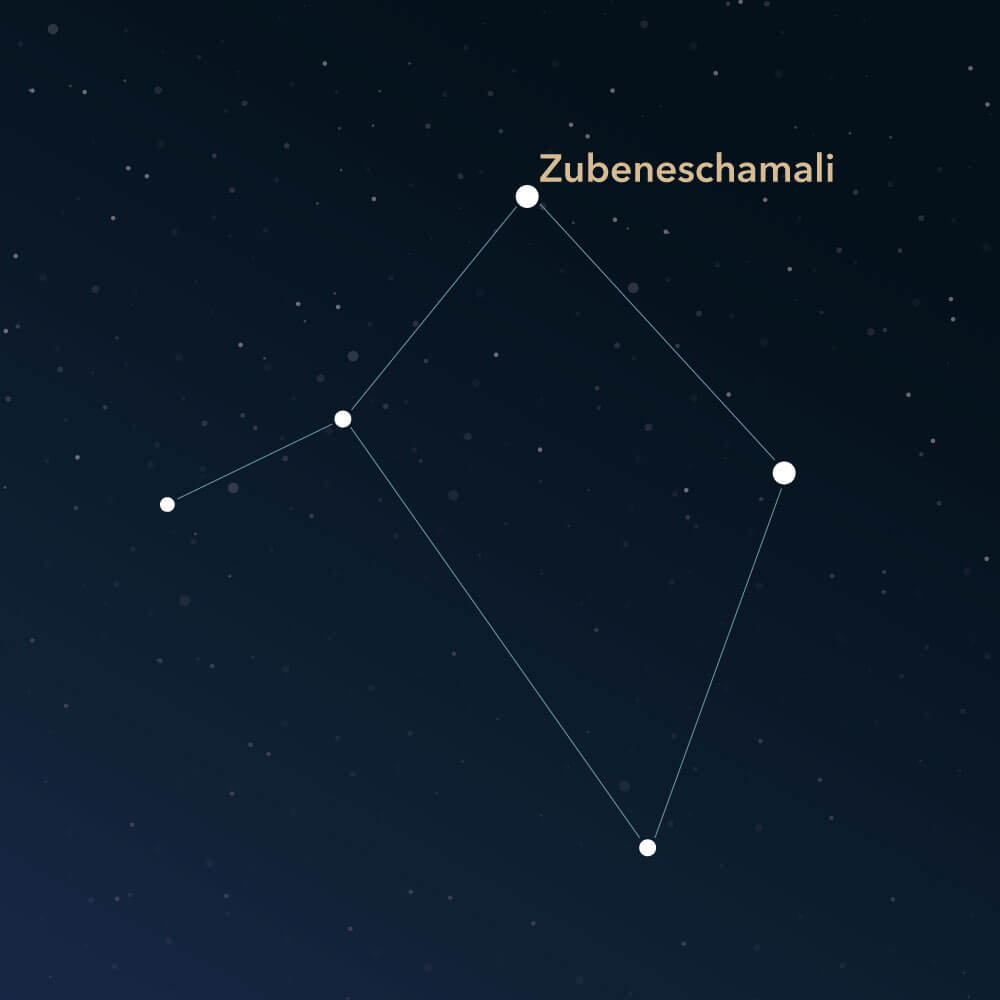
- Zubeneschamali (HIP number 74785)
- Specialties
- Globular cluster, galaxies
The constellation Libra symbolizes weighing scales or a balance. It is a constellation in the southern sky and is particularly known in astrology. It is one of the 48 ancient constellations described by the Greco-Roman astronomer Claudius Ptolemy. There are only faint deep-sky objects in this area of the sky that can be observed with professional equipment.
Hemisphere, visibility, and area
Libra is located immediately south of the celestial equator and can therefore be seen in many places. It is visible from anywhere in the southern hemisphere. North of the equator, it is visible up to the 60th parallel. Thus, it can be observed from all regions south of, for example, Helsinki in Finland, St. Petersburg in Russia, or the southern tip of Greenland.
In addition, the constellation is located on the ecliptic. This means that the sun and other planets, such as the moon, pass through the constellation at the same time each year. Therefore, Libra is one of the 12 zodiac signs and is the basis for the astrological sign of Libra.
According to astrology, every living being born between September 24 and October 23 has the zodiac sign Libra. However, this period differs from the current path of the sun. Due to the precession of the earth, the path of the sun has shifted by about one month over the millennia. Today, the sun is in the constellation Libra from October 31 to November 23. At this time, the constellation cannot be seen from earth, as it rises and sets with the sun on the horizon.
The best time to observe Libra in the night sky is between the months of January and August. However, Libra is not a particularly large or conspicuous constellation. With its size of around 538 square degrees, it ranks 29th among the other 88 constellations.
The stars are not particularly bright. Only two stars have an apparent magnitude brighter than 3. The most shining star is named Zubeneschamali (Latin: β Librae, Beta Librae), which comes from Arabic and means "the northern claw." It is a green shining star about 185 light-years from earth. Its apparent brightness is roughly 2.6.
The second brightest star also bears an Arabic name. It is called Zubenelgenubi (Latin: α Librae, Alpha Librae), which means “the southern serpent.” The star is just slightly darker, with an apparent brightness of roughly 2.75. Its distance to earth is about 76 light-years.
To find Libra in the night sky, it can be helpful to orient oneself to the adjacent constellations. In the immediate vicinity are the Serpens (Cauda, Head), the Hydra (commonly known as water snake), as well as the Lupus and the Ophiuchus (known as serpent bearer). Along the ecliptic, the two constellations Virgo and Scorpius are adjacent, which are also part of the astrological zodiac signs.
Furthermore, an alternative method for locating the Libra is to take into account the moon's position. At certain predictable times, the moon moves across the Libra constellation. Therefore, it can be helpful to consult a lunar calendar to determine which nights the moon will be passing through Libra.
Specialties in the constellation
In the area of Libra, there is a globular cluster and some very faint galaxies that can only be perceived with professional equipment, such as telescopes and prism binoculars.
The globular cluster is cataloged as NGC 5897. It has an apparent brightness of around 8.6 and is located about 40,000 light-years away from the Milky Way. It is a very loosely structured star cluster since even the star density in its center is very low. The object was discovered by the German-British astronomer William Herschel in March 1785.
History
It is said that the Sumerians named the constellation after the balance because, in their time, the sun was in the constellation during the equinox. The Babylonians and ancient Greeks associated the sign with the Scorpion's claws. The same was true for Arabic astronomers. In Greek, the constellation was called "Chelai" (English: claws).
It wasn't until around 100 AD that the constellation was introduced with the current name by the Romans and included in the zodiac. They saw it as the balance of Astraea, the Roman goddess of justice. Like back then, it is still regarded today as a symbol of justice.
It is not possible to determine exactly who first described the constellation of Libra. However, there are copies of the Roman-Greek astronomer Claudius Ptolemy's work in which Libra appears as a constellation.
Constellation Visibility Tool
Los Angeles, USA
34.05°, -118.24°
Constellation Observing Guide
This guide shows when the constellation is visible above the horizon and provides the optimal viewing window when the sky is darkest. Times are displayed in the location's timezone (PDT).
🎯 Best Observing Window
Optimal time when the constellation is fully visible AND the sky is at its darkest. Perfect for telescopic observations, astrophotography, and viewing faint details.
Optimal start
21:14
Jun 6, 21:14
Optimal end
03:42
Jun 7, 03:42
Duration
6.46h
Prime observing time
✨ Perfect Observing Conditions
This is the overlap when the constellation is above horizon AND the sky is at its darkest. Ideal for telescopic observations and photography.
Constellation Visibility from Your Location
5
Visible Stars
0
Never Rise
0
Always Up
100%
Visible
All stars of this constellation can be observed from your location
Constellation Visibility
When the constellation is above the horizon (includes daylight hours)
Rises
17:24
Jun 6
Fully Up
18:29 – 03:42
Jun 6
Starts Setting
03:42
Jun 7
Fully Set
04:59
Jun 7
Above Horizon Times
Includes daylight hours when stars aren't visible to naked eye.
Astronomical Night
When the sky is darkest (sun >18° below horizon)
Dark sky begins
21:14
Jun 6
Dark sky ends
04:34
Jun 7
Darkest Sky Period
Sun more than 18° below horizon. Best for faint objects.
Observing Tips
Read more interesting articles

An overview of all 88 constellations
Learn more about all 88 constellations and read interesting information about the mythology, visibility, and features.

Planetarium App
Discover the night sky with our planetarium app!
Available for iOS and Android.
Name a star in the constellation Libra
Name a star in a constellation and create something that lasts for eternity.