The constellation Pyxis
Characteristics
- Other names / Symbolism
- Compass
- Hemisphere
- Southern hemisphere
- Visibility
- January - March
- Area
- 221 deg²
- Brightest star
- α Pyxidis (HIP number 42828)
- Specialties
- Open star clusters, planetary nebula, galaxy
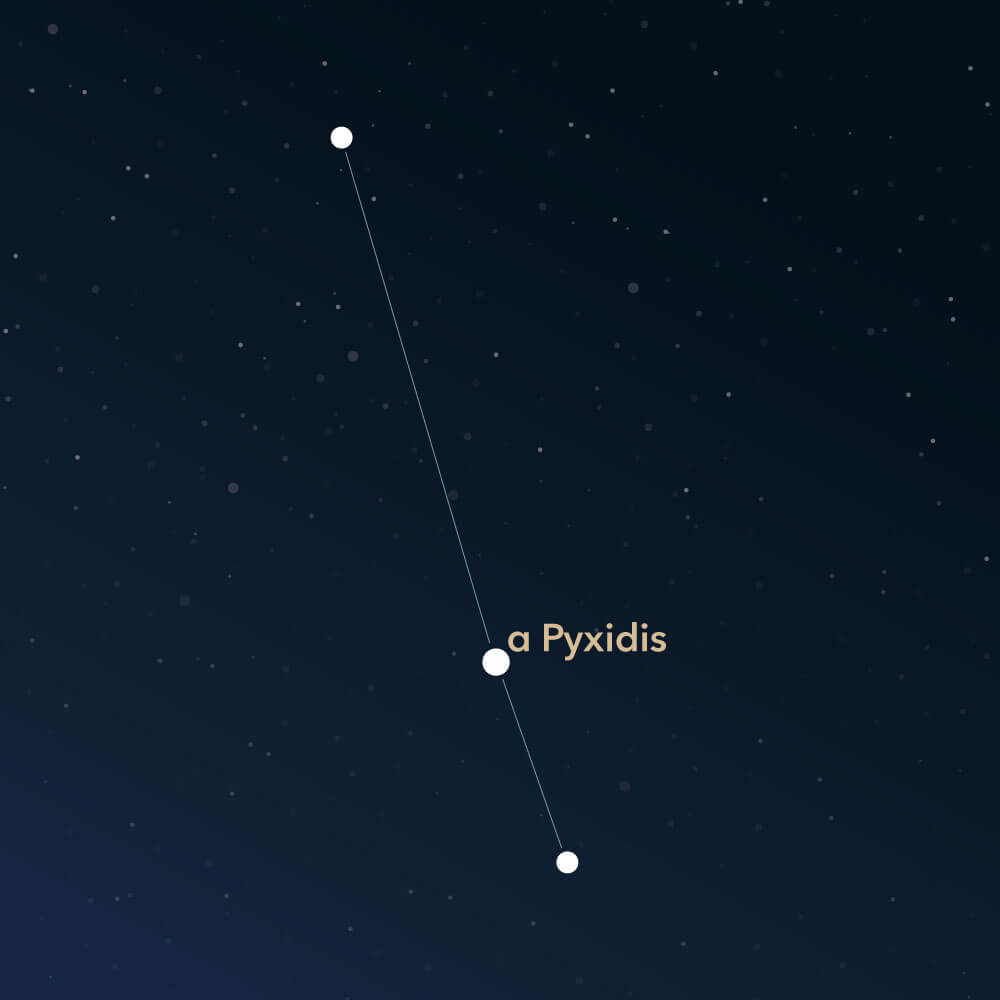
The Pyxis, known as Compass, is a small and inconspicuous constellation in the southern sky. It was introduced by the French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in the mid-18th century. There are only a few deep-sky objects located in this area.
Hemisphere, visibility, and area
The constellation Pyxis lies in the southern hemisphere and is visible from many places. While it is fully visible in the night sky for all regions south of the equator, it can be observed up to the 53rd parallel in the northern hemisphere. This corresponds to places such as Hamburg in Germany or Edmonton in Canada.
The months of January to March offer the best conditions for observing the constellation. It stretches over about 221 square degrees in the night sky and is ranked 65th in terms of size compared to all other 88 constellations.
However, finding the Pyxis is not easy, as there are only faint stars in its area. In most visualizations, the three main stars are connected in a straight line. The brightest star is α Pyxidis (Alpha Pyxidis), with an apparent magnitude of only 3.68. It is located about 1,200 light-years away.
To still discover the Pyxis, it is helpful to orient oneself to the surrounding constellations. To the north lies Hydra, and to the east is Vela. Southern Puppis is located, and to the west Antlia is situated.
Specialties in the constellation
In the constellation area lies the Milky Way band, which provides for open star clusters, a galaxy and a planetary nebula.
The planetary nebula NGC 2818 is the brightest object, with an apparent magnitude of roughly 8.2. It was discovered by the Scottish astronomer James Dunlop in May 1826.
The open star cluster with the catalog number NGC 2627 is only slightly fainter. It has an apparent magnitude of about 8.4. It was found by the German-British astronomer William Herschel in March 1793.
Just a few years earlier, he also discovered the spiral galaxy NGC 2613. It has an apparent magnitude of approximately 10.4, and its distance from the Milky Way is estimated to be about 66 million light years.

History
The French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille measured the positions of over 10,000 stars between 1750 and 1754 and subsequently defined several new constellations, including the Pyxis, often just called Compass.
During his sky survey conducted near Cape Town in South Africa, he found that the ancient constellation Argo Navis was too large and unwieldy. Therefore, he divided it into the three constellations of Carina (the keel), Vela (the sails), and Puppis (the stern). In doing so, he discovered the stars of the Pyxis and classified them accordingly.
In the 19th century, the son of German-British astronomer William Herschel proposed renaming the constellation as the mast of the ship to honor the ancient constellation of Argo Navis, but this suggestion was never adopted.
Constellation Visibility Tool
Los Angeles, USA
34.05°, -118.24°
Constellation Observing Guide
This guide shows when the constellation is visible above the horizon and provides the optimal viewing window when the sky is darkest. Times are displayed in the location's timezone (PDT).
🎯 Best Observing Window
Optimal time when the constellation is fully visible AND the sky is at its darkest. Perfect for telescopic observations, astrophotography, and viewing faint details.
Optimal start
03:20
Oct 22, 03:20
Optimal end
06:12
Oct 22, 06:12
Duration
2.87h
Prime observing time
✨ Perfect Observing Conditions
This is the overlap when the constellation is above horizon AND the sky is at its darkest. Ideal for telescopic observations and photography.
Constellation Visibility from Your Location
3
Visible Stars
0
Never Rise
0
Always Up
100%
Visible
All stars of this constellation can be observed from your location
Constellation Visibility
When the constellation is above the horizon (includes daylight hours)
Rises
N/A
N/A
Fully Up
N/A
Starts Setting
11:41
Oct 21
Fully Set
12:22
Oct 21
Above Horizon Times
Includes daylight hours when stars aren't visible to naked eye.
Astronomical Night
When the sky is darkest (sun >18° below horizon)
Dark sky begins
19:12
Oct 21
Dark sky ends
06:12
Oct 22
Darkest Sky Period
Sun more than 18° below horizon. Best for faint objects.
Observing Tips
Read more interesting articles

An overview of all 88 constellations
Learn more about all 88 constellations and read interesting information about the mythology, visibility, and features.

Planetarium App
Discover the night sky with our planetarium app!
Available for iOS and Android.
Name a star in the constellation Pyxis
Name a star in a constellation and create something that lasts for eternity.