The constellation Aquila
Characteristics
- Other names / Symbolism
- The Eagle
- Hemisphere
- Both Hemispheres
- Visibility
- May - September
- Area
- 652 deg²
- Brightest star
- Altair (HIP number 97649)
- Specialties
- Planetary nebulae, star clusters, galaxies, dark cloud
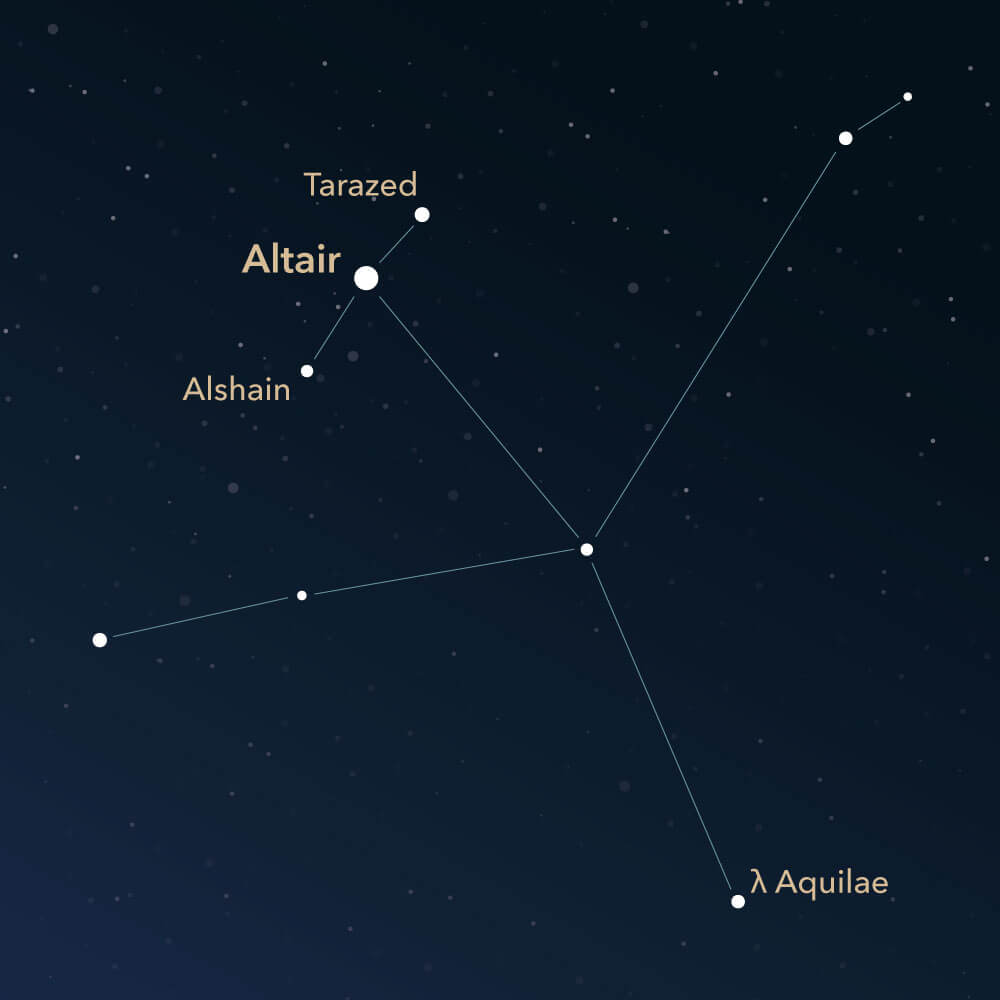
Aquila, also known as The Eagle, is one of the 48 ancient constellations described by the Greco-Roman astronomer Claudius Ptolemy. It is a very prominent and striking constellation, mainly due to a particular star. However, some deep-sky objects also make it very interesting.
Hemisphere, visibility, and area
The constellation Aquila stretches across the celestial equator and can therefore be observed from both hemispheres. It is visible from all locations between 79° N and 72° S latitudes, making it viewable worldwide except for particularly northern and southern regions. The best time to observe Aquila is from May to September.
The constellation has an area of about 652 square degrees, making it the 22nd largest compared to all other 88 constellations.
Although the constellation is only visualized with three bright stars, it is easy to find. Together with the constellations Lyra and Cygnus, it forms the well-known Summer Triangle. This consists of the brightest stars (Vega, Deneb, and Altair) of the most prominent constellations in the summer and autumn skies.
Altair (Latin: α Aquilae, Alpha Aquilae) is the brightest star in the constellation Aquila. It has an apparent magnitude of approximately 0.76, making it the twelfth brightest star in the entire night sky. Tarazed (Latin: γ Aquilae, Gamma Aquilae) and Alshain (Latin: β Aquilae, Beta Aquilae) are the two other bright stars. They are located above and below Altair, forming the head of Aquila.
Aquila borders a total of nine other constellations, including Sagitta, Hercules, Ophiuchus, Serpens (Tail), Scutum, Sagittarius, Capricornus, Aquarius, and Delphinus.
Specialties in the constellation
The band of the Milky Way passes through Aquila, providing many exciting objects. There are several planetary nebulae, open star clusters, and globular clusters in the area of the constellation. A barred spiral galaxy and a dark cloud can also be observed. Additionally, there is a supernova remnant and a high-velocity cloud.
One of around ten planetary nebulae in Aquila is NGC 6751, also known as the Glowing Eye Nebula. It received its name because it resembles an iris in high-resolution photographs. The planetary nebula is approximately 6,500 light-years away and has a white dwarf as its central star with an apparent magnitude of 14. It is located near the star λ Aquilae.

The brightest open star cluster in Aquila is NGC 6709. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.7 and is roughly 3,500 light-years from earth. A group of around 40 stars can be seen in a smaller telescope. It is located northeast of the neighboring constellation Hercules.
In addition to several open star clusters, the constellation also contains some globular clusters. However, these can only be observed with larger instruments and initially appear as hazy spots.
A barred spiral galaxy can also be found in Aquila. In August 1788, the German-British astronomer William Herschel discovered NGC 6814. It is not exceptionally bright or noticeable, however.
Barnard 142/143, a dark cloud that covers the stars behind it, is located slightly northwest of the star Tarazed. Even with a pair of binoculars, the dark cloud can be perceived, appearing as approximately the size of a full moon.
Mythology
There are several interpretations of the mythological origin of the constellation.
In one version of Greek mythology, the constellation represents the eagle of the Olympic god Zeus, who was given many different tasks. The eagle was responsible for retrieving every lightning bolt Zeus threw to earth, abducting prince Ganymede from Troy, and flying him to Olympus, where he would serve the gods. The eagle was also supposed to protect Zeus from Cupid's arrows, preventing him from falling in love on earth.
According to some stories, the eagle could not perform its duties, so it was memorialized as a constellation in the sky.
Another version tells the story of the eagle Ethon, who ate daily from the liver of the bound Prometheus. Prometheus was immortal and could not escape the pain. Finally, Hercules saved him by killing the eagle with a poisoned arrow.
PublishedRead more interesting articles

An overview of all 88 constellations
Learn more about all 88 constellations and read interesting information about the mythology, visibility, and features.

Planetarium App
Discover the night sky with our planetarium app!
Available for iOS and Android.
Name a star in the constellation Aquila
Name a star in a constellation and create something that lasts for eternity.