The constellation Volans
Caractéristiques
- Nom latin
- Volans
- Hémisphère
- Hémisphère sud
- Visibilité
- December - February
- Région
- 141 deg²
- Étoile la plus brillante
- β Volantis (HIP number 41312)
- Spécialités
- Galaxies
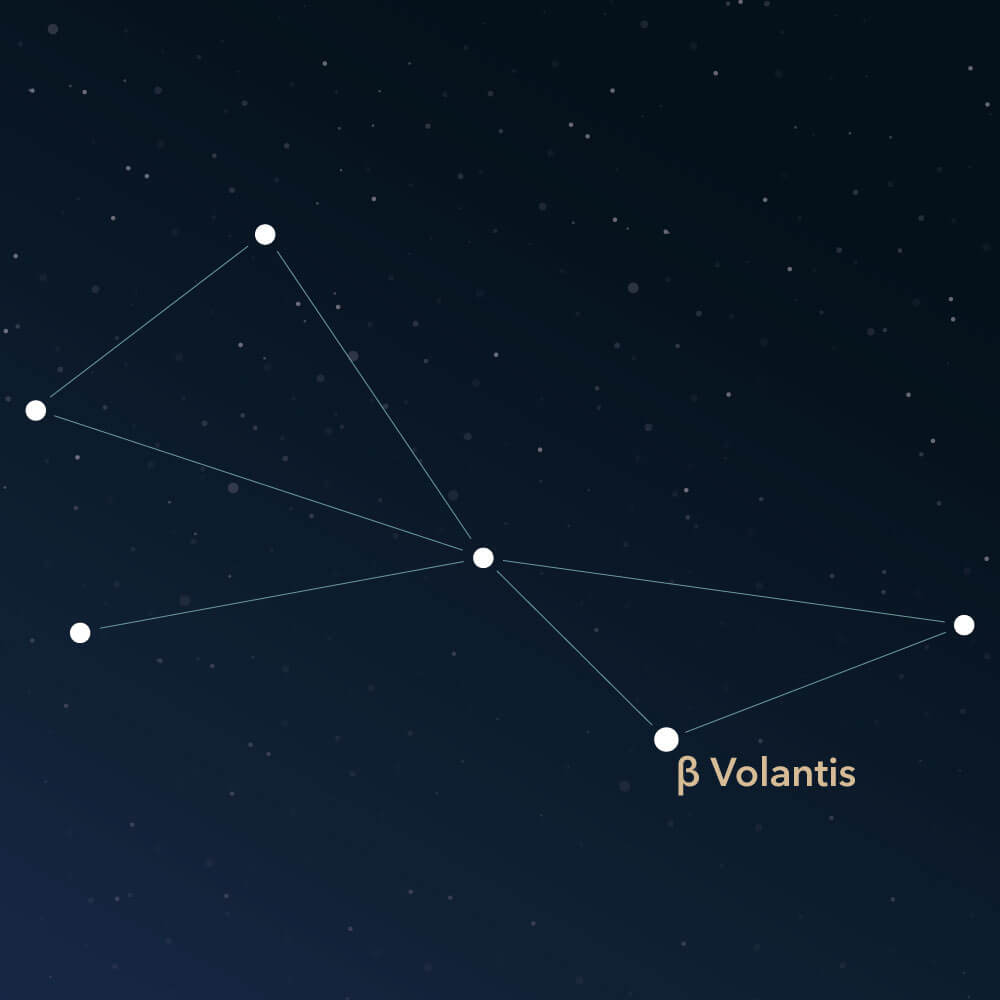
Volans symbolizes a flying fish. The term is widely used for this constellation. It lies in the southern sky and is very inconspicuous. However, it is easy to find in the night sky and contains a few exciting deep-sky objects.
Hemisphere, visibility, and area
The Volans is located in the southern hemisphere and can be seen from all places on the south half of the earth. However, it is only visible north of the equator up to the 14th latitude, corresponding to places such as El Salvador, the group of islands Cape Verde, or Bangkok in Thailand.
December to February offers the best conditions for observing the Volans in the night sky.
The constellation covers an area of 141 square degrees, making it one of the smallest in the night sky. In comparison to the other 88 constellations, it ranks 76th in size.
There are different visualizations of the Volans. In many depictions, two triangles are opposite each other, with a chain of stars coming out of the center. The triangles represent the wings, and the chain of stars represents the fish's body. Other images show the Volans as an irregular quadrilateral with a chain of stars.
There are no particularly prominent stars in the constellation. None of them are brighter than the third magnitude. The brightest star has an apparent magnitude of only 3.77 and is a luminous orange star about 108 light-years away. Its name is β Volantis (Beta Volantis).
To find the constellation in the night sky, it is worth looking for the very bright star Miaplacidus (Latin: β Carinae, Beta Carinae). Because this star is located near the Volans and is part of the neighboring constellation Carina. Other neighboring constellations are Pictor and Dorado, as well as Mensa and Chamaeleontis.
Specialties in the constellation
The Volans contains a couple of interesting galaxies; a barred spiral galaxy, a spiral galaxy, and a ring galaxy.
The barred spiral galaxy NGC 2442 (or NGC 2443) is also known by the unusual name of the Meathook Galaxy or Cobra and Mouse. It was discovered in December 1834 by the British astronomer John Herschel.
It consists of two asymmetrical spiral arms that are connected in an S-shape. Young stars make parts of the nebula regions glow red while other areas shine in shades of purple. The distance of the barred spiral galaxy from the Milky Way is estimated to be 56 million light-years. It has a diameter of approximately 120,000 light-years.

In contrast, the spiral galaxy NGC 2397 has a diameter of only about 40,000 light-years. It is located about 52 million light-years away from the Milky Way and was also found by the British astronomer John Herschel. The core consists mainly of older stars in yellow and red, while the outer arms consist primarily of younger, bluish stars and dust clouds.
History
At the end of the 16th century, when a Dutch fleet first traveled to the legendary Spice Islands to establish new trade relations, the crew had another important task.
The astronomer Peter Plancius wanted more precise data on the stars, so the cartographer Frederick de Houtman and the Dutch navigator Pieter Dierkzoon Keyser measured the positions of 135 stars.
From this data, 12 new constellations were defined, including the Volans. The inspiration for this constellation came from the flying fish they encountered on their journey.
PubliéLire d'autres articles intéressants

An overview of all 88 constellations
Learn more about all 88 constellations and read interesting information about the mythology, visibility, and features.

Application Planétarium
Découvrez le ciel nocturne avec notre application de planétarium !
Disponible pour iOS et Android.
Nommez une étoile dans la constellation Flying Fish
Name a star in a constellation and create something that lasts for eternity.