The constellation Octans
Caractéristiques
- Nom latin
- Octans
- Hémisphère
- Hémisphère sud
- Visibilité
- All year round
- Région
- 291 deg²
- Étoile la plus brillante
- ν Octantis (HIP number 107089)
- Spécialités
- Galaxies, open star clusters
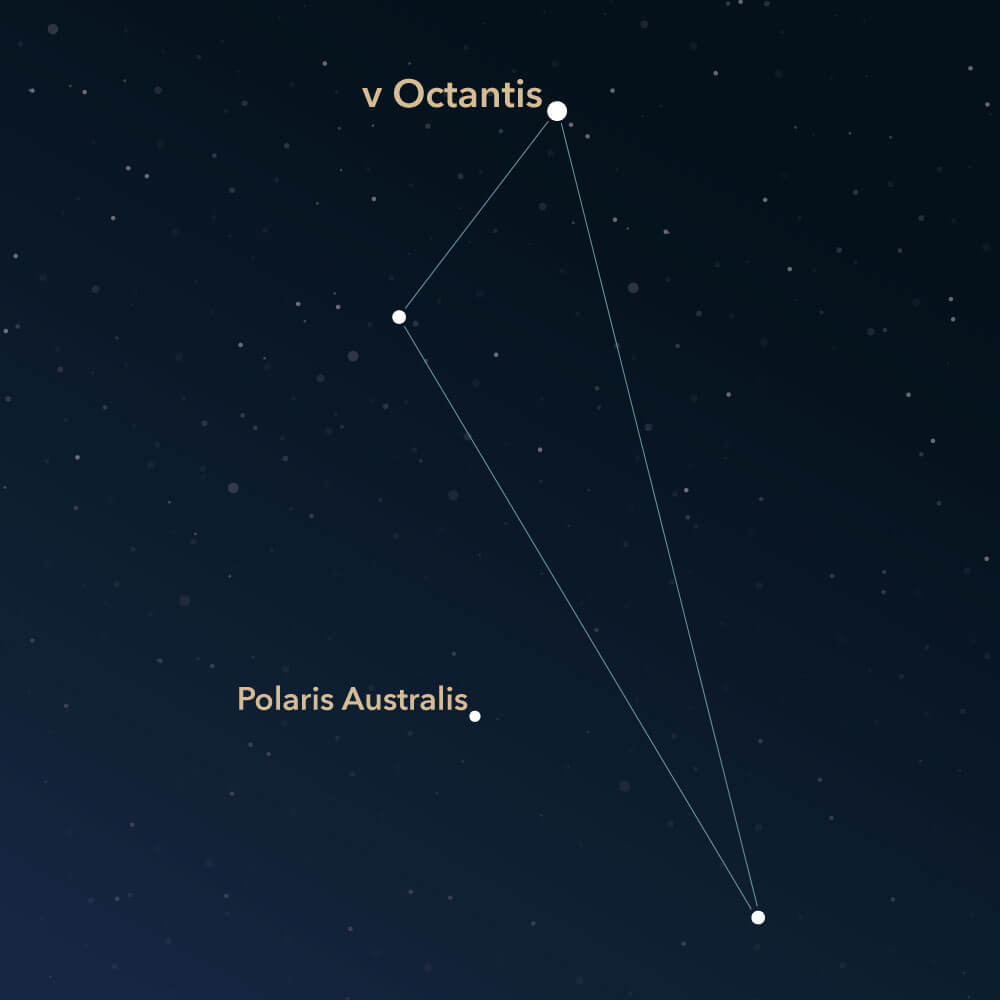
The Octans symbolizes an octant, a navigation instrument. It is an inconspicuous constellation at the south celestial pole. Due to its location, it is often referred to as the counterpart to the Ursa Minor (commonly known as Little Bear or Little Dipper), which is located at the northern celestial pole. There are no deep-sky objects visible to the naked eye situated within its area.
Hemisphere, visibility, and area
The Octans constellation is located near the celestial south pole in the southern sky and is, therefore, almost exclusively visible from the southern hemisphere. It can only be observed in its entirety from locations north of the equator up to the 6th parallel, such as Medellin in Colombia or the far south of Sri Lanka.
For all regions in the southern hemisphere, the constellation is circumpolar, meaning it can be observed year-round.
The Octans stretches across an area of approximately 291 square degrees in the night sky, and it ranks 50th in size among all 88 constellations.
Finding the constellation in the night sky is not easy, as there are few bright stars within its area. This is a significant difference from the counterpart Ursa Minor, which has the prominent star Polaris as a useful guide near the northern celestial pole. By contrast, there is only one star with an apparent magnitude of 5 or brighter near the southern celestial pole, known as Polaris Australis, which is not included in the visualizations of the constellation. Only the three main stars are connected to form a triangle, with the brightest being the orange star ν Octantis (Nu Octantis), which has an apparent magnitude of roughly 3.76 and is located approximately 69 light-years away.
The Octans is surrounded by seven other constellations, including the Indus, the Pavo, the Apus, and the Chamaeleontis. It also has direct neighbors such as the Mensa, the Hydrus, and the Tucana.
Specialties in the constellation
In the area of the star constellation are several galaxies as well as an open star cluster. However, professional equipment such as a telescope is required to observe them.
One of the galaxies is the barred spiral galaxy NGC 7098. It was discovered in September 1835 by the British astronomer John Herschel. Its distance from the Milky Way is estimated to be around 101 light-years, and its diameter is believed to be about 130,000 light-years.

History
In the mid-18th century, French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille used the invention of the telescope to determine the positions of 10,000 stars from the Cape of Good Hope near Cape Town in South Africa. In doing so, he identified some previously undefined areas of the sky and introduced new constellations.
He drew inspiration for the names of these constellations from technological and artistic innovations, a notable difference from the ancient constellations, which were often named after figures from Greek mythology.
In 1752, he introduced the Octans constellation. It is said to resemble a device utilized for measuring angles, which was used in navigation to determine positions. German astronomer Johann Elert Bode referred to it as "Octans Nautica" around 50 years later.
Constellation Visibility Tool
Los Angeles, USA
34.05°, -118.24°
Constellation Observing Guide
This guide shows when the constellation is visible above the horizon and provides the optimal viewing window when the sky is darkest. Times are displayed in the location's timezone (PDT).
No Optimal Window Found
The constellation's visibility doesn't overlap with the darkest part of the night during the next 48 hours.
Alternative Viewing Options
You can still observe the constellation when it's above the horizon, but there may be some twilight interference. Consider checking again in a few days as visibility patterns change throughout the year.
Constellation Visibility from Your Location
0
Visible Stars
3
Never Rise
0
Always Up
0%
Visible
3 stars are too far south to be visible from your latitude (34.1°N)
Constellation Visibility
When the constellation is above the horizon (includes daylight hours)
Rises
Never Rises
Never Rises
Fully Up
Never Rises
Starts Setting
Never Rises
Never Rises
Fully Set
Never Rises
Never Rises
Above Horizon Times
Includes daylight hours when stars aren't visible to naked eye.
Astronomical Night
When the sky is darkest (sun >18° below horizon)
Dark sky begins
21:25
Jul 2
Dark sky ends
04:45
Jul 3
Darkest Sky Period
Sun more than 18° below horizon. Best for faint objects.
Observing Tips
Lire d'autres articles intéressants

An overview of all 88 constellations
Learn more about all 88 constellations and read interesting information about the mythology, visibility, and features.

Application Planétarium
Découvrez le ciel nocturne avec notre application de planétarium !
Disponible pour iOS et Android.
Nommez une étoile dans la constellation Octant
Name a star in a constellation and create something that lasts for eternity.