The constellation Vela
Características
- Nombre latino
- Vela
- Hemisferio
- Hemisferio sur
- Visibilidad
- January - March
- Área
- 500 deg²
- Estrella más brillante
- γ Velorum (HIP number 39953)
- Especialidades
- Open star clusters, globular clusters, planetary nebulae
The Vela, Latin for Sails of the Ship, is a prominent constellation in the southern celestial sky. Originally, it was part of the Argo Navis constellation (Latin: Ship Argo), which was described by the ancient Greek-Roman astronomer Claudius Ptolemy. There are some interesting deep-sky objects located in this area.
Hemisphere, visibility, and area
The constellation Vela lies in the southern hemisphere and can be observed from the entire southern half of the earth. North of the equator, it is fully visible up to the 32nd latitude, which includes places such as Marrakesh in Morocco, Dallas in the United States, or Shanghai in China.
The months of January through March offer the best view of this constellation, which stretches across approximately 500 square degrees of the night sky.
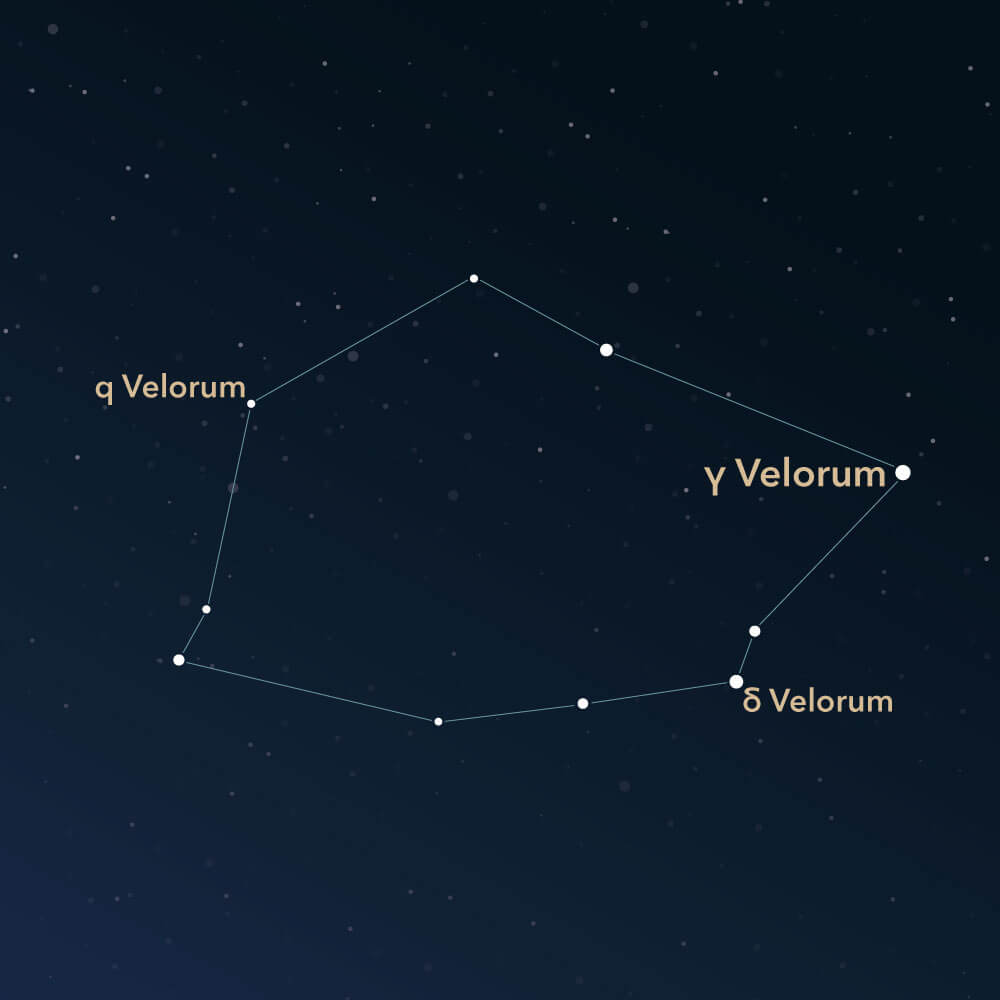
Vela is represented in sky maps by a handful of stars that are connected to form a square or rectangular shape. Five of these stars have an apparent magnitude brighter than 3 and are easily visible in the sky.
The brightest star in Vela, with an apparent magnitude of approximately 1.8, is named γ Velorum (Gamma Velorum). It is a binary star system located about 1,000 light-years away.
Vela is surrounded by five other constellations in the night sky. To the north are the Antlia and the Pyxis, while to the east and south are the Puppis and the Carina. The Centaurus borders Vela to the west.
Specialties in the constellation
Within the area of the Vela constellation lies the Milky Way, which is responsible for several open star clusters, globular clusters, and a planetary nebula.
The brightest open star cluster is known as IC 2391 or the Omicron Velorum Cluster. This cluster is estimated to be around 50 million years old and is located approximately 500 light-years away from earth. It has an apparent magnitude of roughly 2.6 and can be seen with the naked eye, located northeast of the star δ Velorum (Delta Velorum).
The planetary nebula NGC 3132 is also known as the Eight-Burst Nebula. It is estimated to be located around 2,000 light-years away from the sun. At the center of the nebula is a double-star system, with the central star visible through a small telescope. The object is located northeast of the star q Velorum.

Mythology
As part of the Argo Navis constellation, the Vela constellation was included in the 48 ancient constellations by Claudius Ptolemy. It wasn't until 1763 that it was given its own constellation by French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille. Lacaille found the larger Argo Navis constellation to be too cumbersome, so he divided it into the Vela (the sails), the Puppis (the stern), and the Carina (the keel).
Argo Navis was the talking ship of the hero Jason, with whom he sailed to Colchis. There, with the help of Hercules and the twins Castor and Pollux (known as the constellation Gemini), he attempted to steal the Golden Fleece, the skin of the sacrificed ram (constellation Aries).
Jason had been deprived of his throne by his half-brother Pelias. To regain his throne, he was tasked with bringing Pelias the Golden Fleece. This seemed like an impossible feat, as the Golden Fleece was guarded by a dragon in a sacred grove.
Ultimately, the king's daughter Medea helped the hero obtain the Golden Fleece. In honor of all involved, the Argo Navis and the Golden Fleece were immortalized as constellations in the sky.
PublicadoLeer más artículos interesantes

An overview of all 88 constellations
Learn more about all 88 constellations and read interesting information about the mythology, visibility, and features.

Planetario App
¡Descubre el cielo nocturno con nuestra aplicación de planetario!
Disponible para iOS y Android.
Nombrar una estrella en la constelación Sails of the Ship
Name a star in a constellation and create something that lasts for eternity.